testssl.sh is pretty much portable/compatible. It is working on every Linux, Mac OS X, FreeBSD distribution, on MSYS2/Cygwin (slow). testssl.sh is a free command line tool which checks a server’s service on any port for the support of TLS/SSL ciphers, protocols as well as some cryptographic flaws.
Key features
- Ease of installation: It works for Linux, Darwin, FreeBSD, NetBSD and MSYS2/Cygwin out of the box: no need to install or configure something, no gems, CPAN, pip or the like.
- Flexibility: You can test any SSL/TLS enabled and STARTTLS service, not only webservers at port 443
- Toolbox: Several command line options help you to run YOUR test and configure YOUR output
- Reliability: features are tested thoroughly
- Verbosity: If a particular check cannot be performed because of a missing capability on your client side, you’ll get a warning
- Privacy: It’s only you who sees the result, not a third party
- Freedom: It’s 100% open source. You can look at the code, see what’s going on and you can change it.
Installation of testssl in Kali Linux –
You can easily install testssl script from githhub directly by typing below command.
Command: git clone –depth 1 https://github.com/drwetter/testssl.sh.git

After complete installation, it will automatically create a directory with the same file name i.e. “testssl.sh“.

Now to simply run this script, type “./testssl.sh“. If it shows some kind of error, then make sure that you must have executed permissions to run thi script, which you can easily change it via “chmod +x testssl.sh“.

Basically testssl script is usually used for scanning the SSL related vulnerabilities like Heartbleed, POODE, BREACH, CRIME, CCS, Ticketbleed etc.
To scan all SSL vulnerabilities, type “./testssl.sh -U <IP/Host>”
Here -U, to scan all SSL vulnerabilities.

To scan the target in default mode, where it will automatically scan the IP/Host wrt Port 443, type “./testssl.sh <IP/HOST>“.
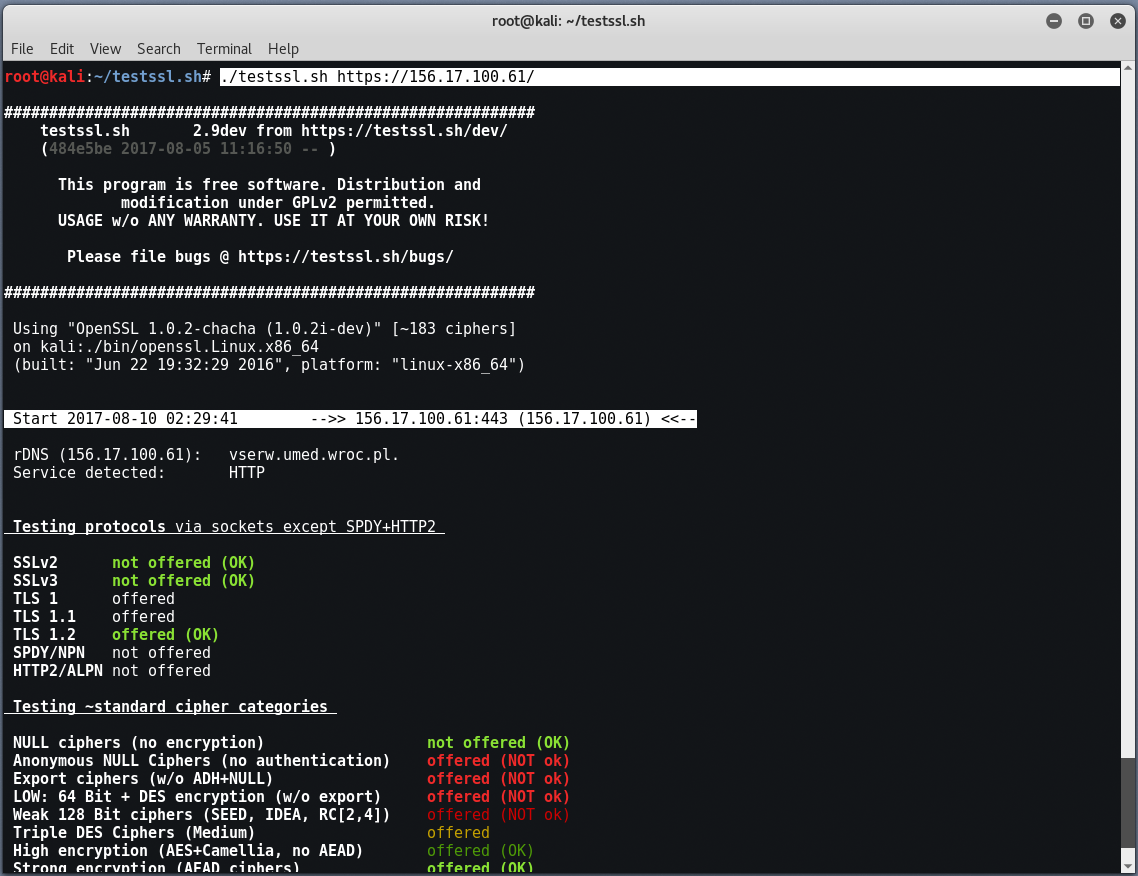
Here is the result in default scanning mode,

Here are the options which you can easily use with testssl script.
- -U, –vulnerable tests all (of the following) vulnerabilities (if applicable)
- -H, –heartbleed tests for Heartbleed vulnerability
- -I, –ccs, –ccs-injection tests for CCS injection vulnerability
- -T, –ticketbleed tests for Ticketbleed vulnerability in BigIP loadbalancers
- -R, –renegotiation tests for renegotiation vulnerabilities
- -C, –compression, –crime tests for CRIME vulnerability (TLS compression issue)
- -B, –breach tests for BREACH vulnerability (HTTP compression issue)
- -O, –poodle tests for POODLE (SSL) vulnerability
- -Z, –tls-fallback checks TLS_FALLBACK_SCSV mitigation
- -W, –sweet32 tests 64 bit block ciphers (3DES, RC2 and IDEA): SWEET32 vulnerability
- -A, –beast tests for BEAST vulnerability
- -L, –lucky13 tests for LUCKY13
- -F, –freak tests for FREAK vulnerability
- -J, –logjam tests for LOGJAM vulnerability
- -D, –drown tests for DROWN vulnerability
- -f, –pfs, –fs, –nsa checks (perfect) forward secrecy settings
Note: Don’t try outdated OpenSSL versions before 1.0! Those versions are deprecated, you likely will not get very far. testssl.sh is not locking those versions out yet but things might not work as expected.